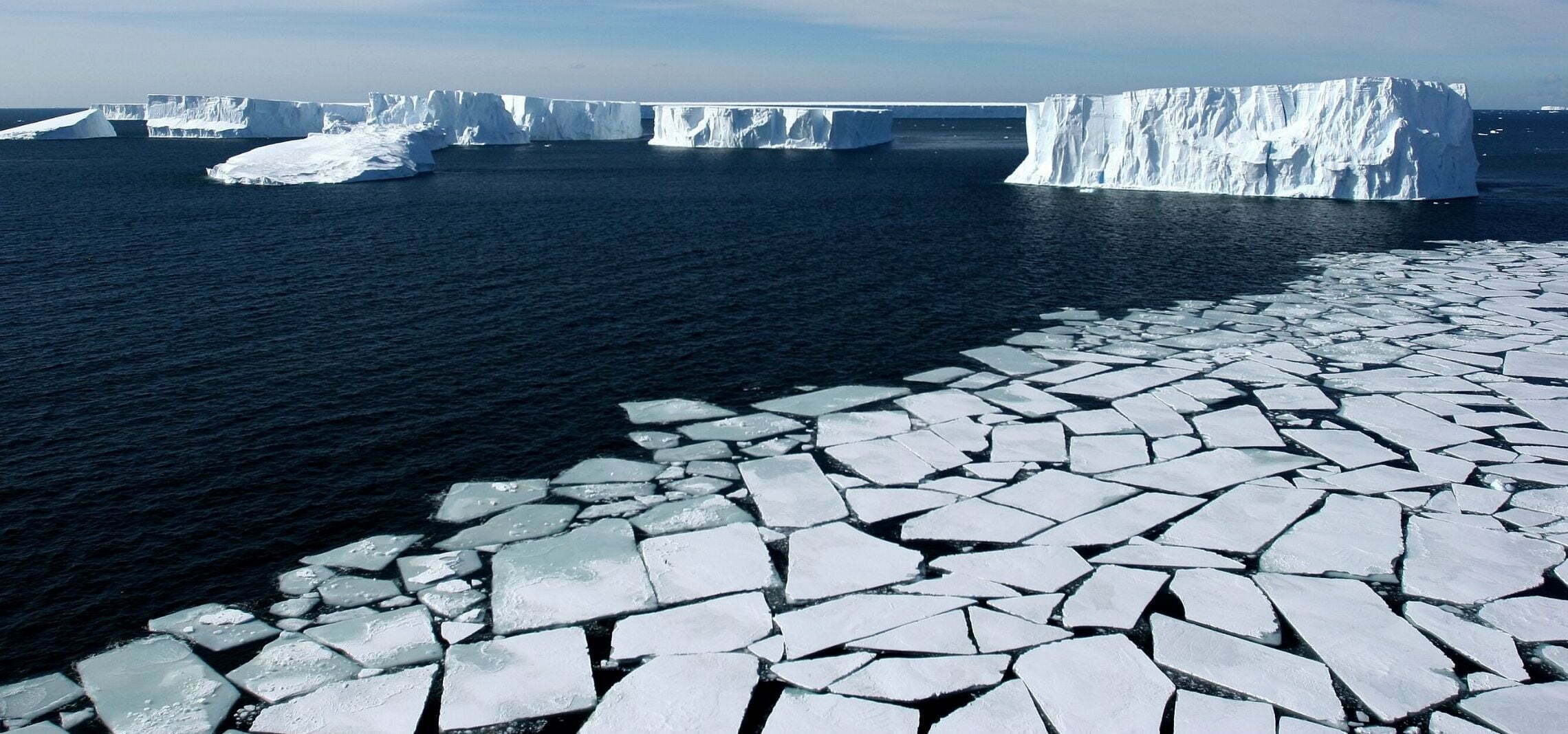
SEA ICE
A story of change
Researchers have been using satellites to monitor sea ice in Antarctica and the Arctic since 1978.
Sea ice cover in the Arctic has been in clear decline for four decades, but trends in Antarctica were less apparent until quite recently.
This changed in 2016, when Antarctic sea ice began to show signs of rapid decline.
A new regime?
CHANGING SEA ICE
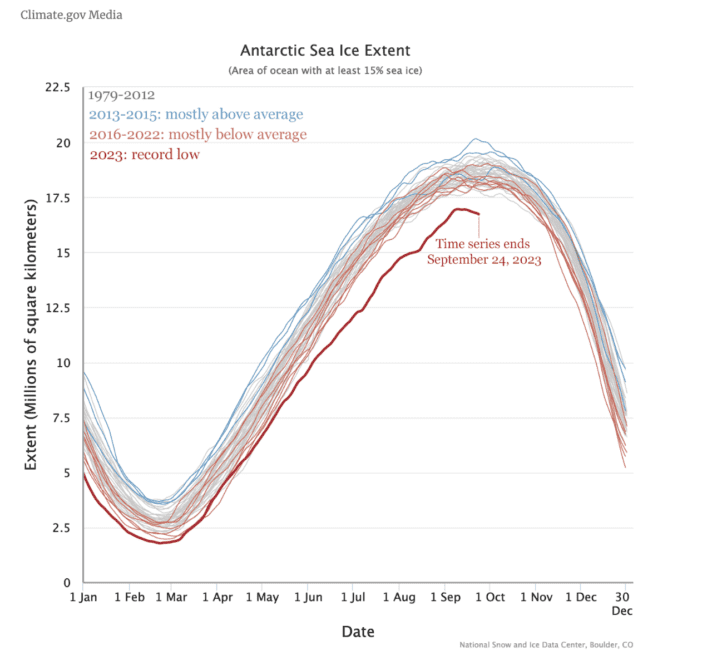
In the summer of 2023 the sea ice around Antarctica dropped to its lowest extent since the satellite record began in 1979. This was the third time the record was broken in only six years.
Extremely low cover continued into the winter, leaving scientists trying to understand the processes behind this sudden change.
A study published in September 2023 shows that warming ocean temperatures may play a role in shifting sea ice towards new lows. It also presents evidence that Antarctic sea ice may be entering a new state, where it becomes more common for ice to form later, cover a smaller area, and melt earlier.
CHANGING SEA ICE
What are the impacts?
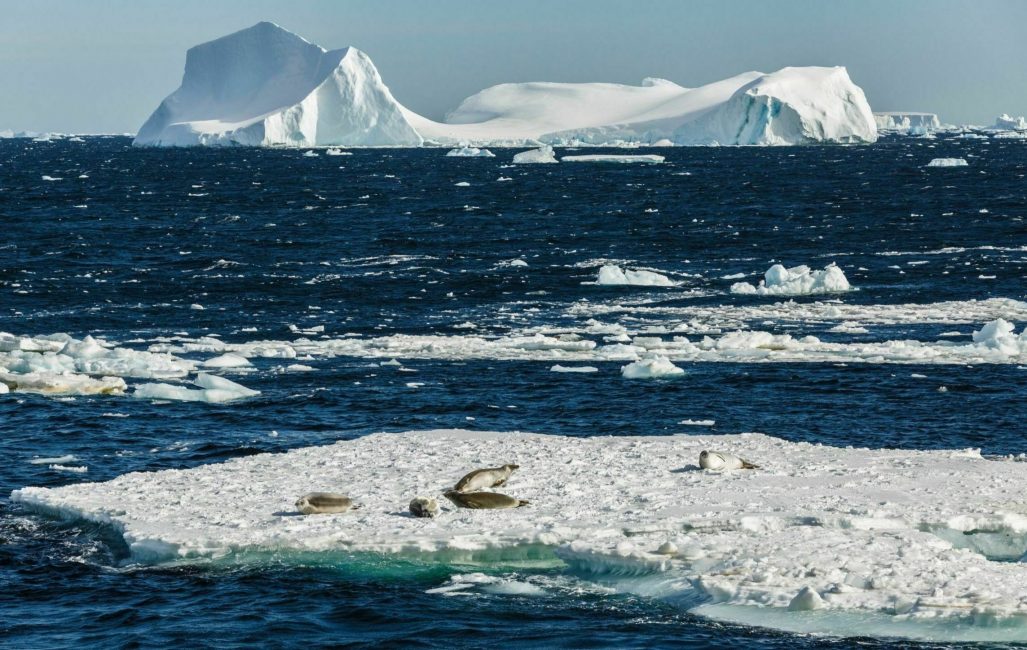
Sea ice is more than just frozen ocean. It is a vital habitat for Antarctic wildlife and plays a critical role in regulating the global climate.
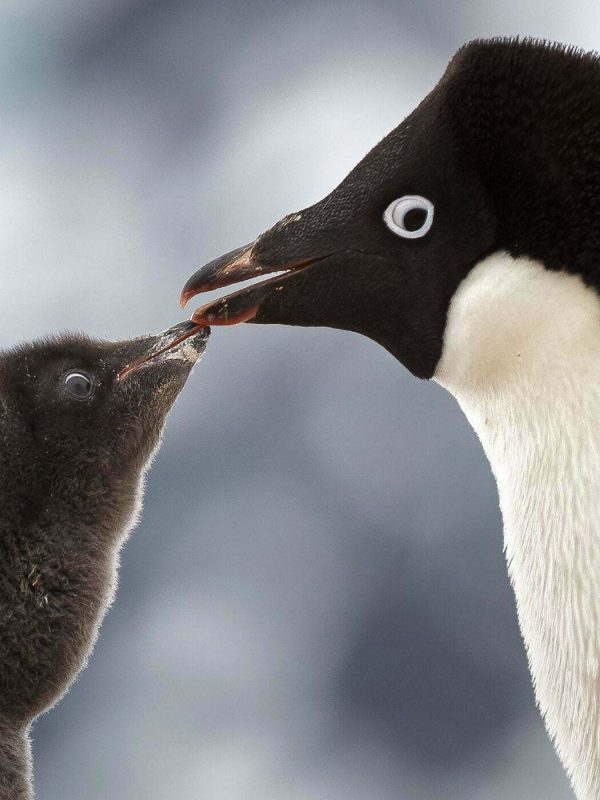

Life
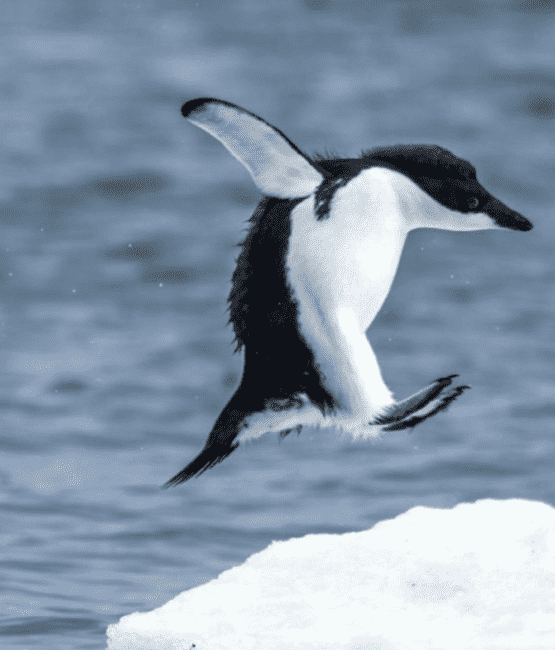
Sea ice is a vital habitat for Antarctic life, from microscopic plants and tiny crustaceans to seals and emperor penguins, the largest penguins on the planet.
Read more

Life
Sea ice is a vital habitat for Antarctic life, from microscopic plants and tiny crustaceans to seals and emperor penguins, the largest penguins on the planet.
Its surface provides refuge for emperor penguins, which rest, moult, breed and raise their chicks on the ice.
Emperor penguins also rely on the vibrant ecosystem that thrives under the ice, where plankton flourish in sheltered nooks and corridors.
There have been several reports of catastrophic breeding failures around Antarctica due to changes in sea ice.

Circulation
Heavy, dense water produced under sea ice plays a vital role in global ocean circulation.
Read more

Circulation
Heavy, dense water produced under sea ice plays a vital role in global ocean circulation.
‘Antarctic Bottom Water’ (AABW) is a by-product of sea ice formation, and is the heaviest, most dense water on the planet, much denser than the water around it.
In 2012, researchers found that the amount of AABW being produced around East Antarctica had reduced by around 60% since the record began in 1970. Over the next five years AABW became warmer, fresher and less dense at an increasing rate.
The exact cause of the freshening is unclear, but it could be linked to reduced sea ice cover. As sea ice cover declines, there may be less AABW produced as a by-product of sea ice formation. It’s also possible that AABW is being diluted by the accelerated melting of ice shelves and ice sheets, which introduce less dense freshwater into the ocean. Both of these things may be occurring at the same time.
Why does this matter?
AABW helps power global ocean circulation, which in turn helps regulate the global climate. Due to its relative density, when AABW is produced it sinks from the surface of the ocean to the depths. This cascading action helps stimulate slow, deep water currents such as the Gulf Stream, that circulate around the globe and regulate our climate.
Fresher, lighter AABW may not sink as rapidly, reducing the strength of its current-pumping effect. This could cause global ocean circulation to slow down or even stop, resulting in chaotic changes to the climate.
There is already growing evidence that major global ocean currents are slowing down in response to the climate crisis, particularly in the northern hemisphere, so researchers are keeping a close eye on Antarctic Bottom Water.
Learn more about the role of AABW and the Southern Ocean in global ocean currents.
You can help
CHANGING SEA ICE
The decline of sea ice is an urgent reminder of the need to act now to reduce the impacts of the climate crisis.
For over 40 years, ASOC has represented the global conservation community at the highest levels of Antarctic governance.
With your support, we continue to work for the strongest possible Antarctic protections, and decisive action to curb the climate crisis.

SEA ICE
How do Antarctic researchers study sea ice?
The Antarctic coastline (including ice) is over thirty thousand miles long, encircling the globe across latitudes from outside the Antarctic Circle to deep within.
How do Antarctic sea ice scientists study seasonal patterns of advance, retreat and duration over such a large area? And what have they observed since the satellite record began in 1978?
Studying Antarctic sea ice cover
CHANGING SEA ICE
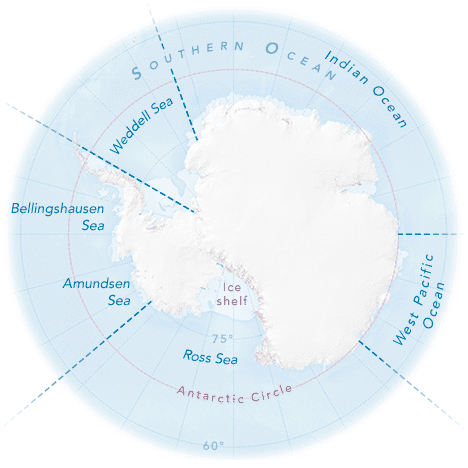
At its winter maximum, Antarctic sea ice can cover an area of around 11 million square miles (18 million sq.km): almost twice the size of the United States of America, and larger than Antarctica itself.
Sea ice covers such a vast area of the Southern Ocean around Antarctica that it spans multiple oceanic and atmospheric zones. Scientists typically divide the Antarctic sea ice area into five sectors to explore the nature and drivers of sea ice change and variability. These sectors are: the Weddell Sea; Bellingshausen and Amundsen Sea; Ross Sea; West Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean sectors.
Arctic vs Antarctica
UNPREDICTABLE SEA ICE
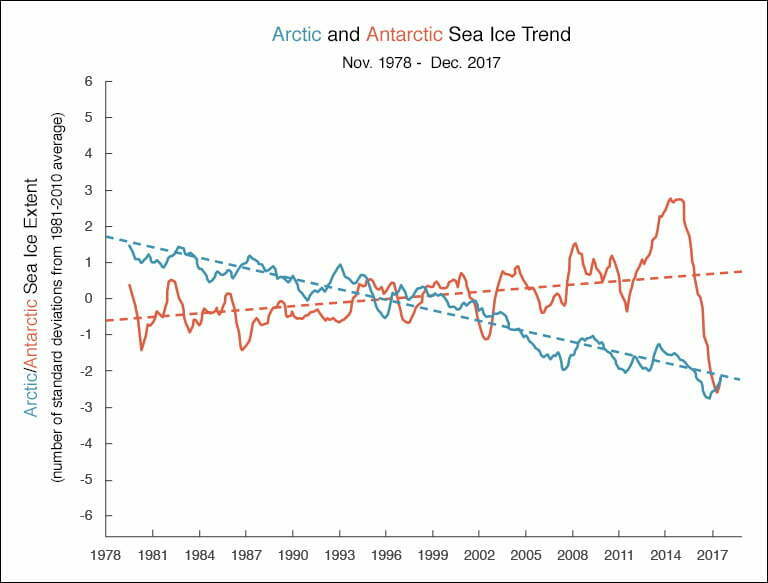
Between 1978 and 2014 scientists were surprised to find that although temperatures were rising globally and Arctic sea ice was in steep decline, sea ice around Antarctica was gradually increasing across four of the five sectors.
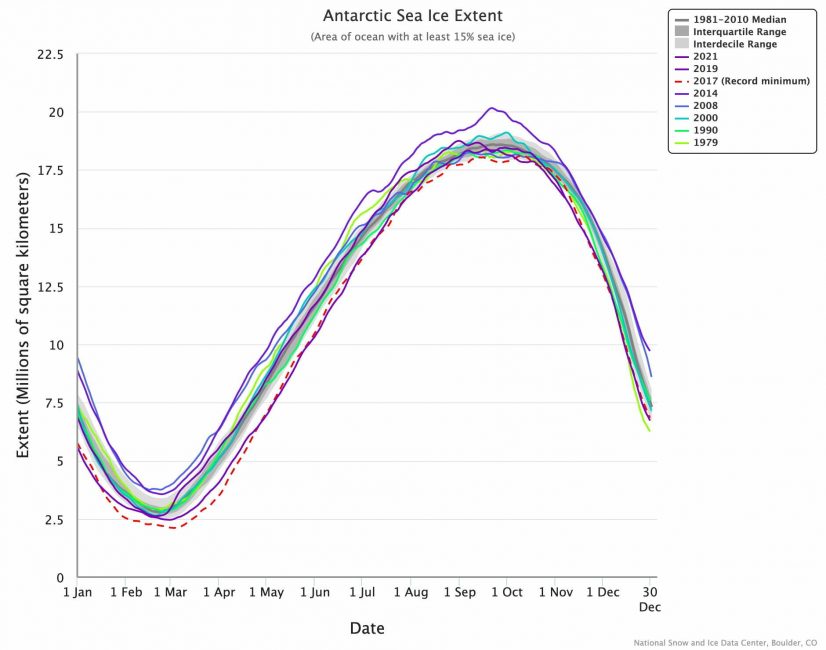
But by 2016 Antarctic sea ice was plummeting, and in 2017 it too hit a record low.
The pace of sea ice decline in Antarctica eclipsed any change recorded in the Arctic.
Within only three years, 35 years of gradual gains had been lost. Researchers are still investigating the causes of this extremely rapid decline.
Antarctic Peninsula Sea Ice Decline
UNPREDICTABLE SEA ICE
While much of Antarctica experienced an increase in sea ice cover before 2014, followed by a rapid decline, the Amundsen/Bellingshausen Sea sector told a very different story.
Sea ice here was in steady decline*.
Upper ocean temperatures in the Bellingshausen Sea, west of the Antarctic Peninsula, have increased by over 2°F (1°C) since 1955.
On the west Antarctic Peninsula between 1978 and 2014, the winter sea ice duration declined by almost 100 days.
*With the exception of the period between 2017 and 2019,
when sea ice in the Amundsen/Bellingshausen Sea sector increased slightly, illustrating the unpredictability and seasonal variability of Antarctic sea ice.
Into the future
CHANGING SEA ICE
Scientists continue to monitor Antarctica’s changing sea ice to build on existing data. They are studying the atmospheric and ocean factors involved, and working on improving the performance of climate models to better predict the changes to come.
One of the many big unknowns at this stage is the thickness distributions of Antarctic sea ice and its snow cover, and whether or not these are changing. Researchers hope this information will emerge from a new suite of satellite altimeter missions in the coming years.

SEA ICE
Help keep sea ice solid
Thanks to the generous support of a global network of Antarctic advocates, ASOC is working at the highest levels of Antarctic governance to push for strong protection for the Antarctic. Join us today.
KEEP LEARNING
Related reading
Scientific consultation: Ted Scambos, Senior Research Scientist at the Earth Science Observation Center of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, and Rob Massom, Sea Ice and Remote Sensing scientist at the Australian Antarctic Program.
Now that you’ve learned about how Antarctic sea ice is changing, read on to learn more about extraordinary Antarctica.
 ASOC
ASOC








